Vomeronasal Organ
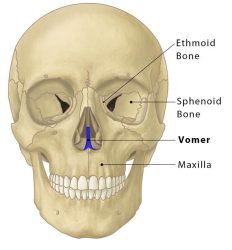
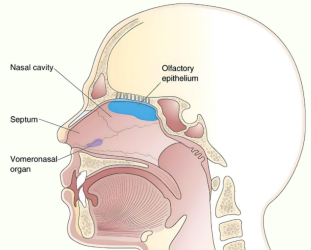
Newsletter Vomeronasal Organ (VNO) What is Vomeronasal Organ? While the human body is filled with intricate structures and organs, there are some that often remain hidden from the limelight. One such organ is the vomeronasal organ (VNO). Nestled deep within the nasal cavity, the Vomeronasal Organ plays a pivotal role in chemical communication and the perception of pheromones. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of the vomeronasal organ, exploring its anatomy, function, and the ongoing debates surrounding its significance in humans. Anatomy of the Vomeronasal Organ The vomeronasal organ is a chemosensory structure found in many vertebrates, including humans, though its presence and functionality are subject to debate. Located within the nasal cavity, the It is situated close to the septum, just above the incisive canal. It consists of two narrow ducts, called the vomeronasal ducts, which open into the nasal cavity through small openings known as vomeronasal pores. Function and Significance The primary function of the Vomeronasal Organ is to detect and process pheromones. Pheromones are chemical signals released by individuals of the same species, which can influence various physiological and behavioral responses in conspecifics. It is highly specialized for detecting these chemical signals, which are important for social and reproductive interactions in many animals. In non-human mammals, the this organ plays a crucial role in mediating various behaviors, such as sexual attraction, territorial marking, and maternal-infant bonding. It is involved in detecting pheromones related to reproductive status, dominance, and social communication. However, the existence and functionality of this organ in humans are subjects of ongoing scientific investigation and debate. Debates and Controversies The presence and functionality of the Vomeronasal Organ in humans have been a topic of controversy within the scientific community. Some researchers argue that while the Vomeronasal Organ develops during embryonic development, it regresses and becomes non-functional in humans, rendering it obsolete in adulthood. They propose that other olfactory structures, such as the main olfactory system, play a more significant role in chemical communication. On the other hand, proponents of the Vomeronasal Organ’s functionality in humans argue that it may still play a role, albeit a diminished one, in mediating subconscious responses to pheromones. They suggest that this organ might contribute to modulating social behaviors, such as mate selection and certain emotional responses. However, further research is needed to reach a definitive conclusion on the exact functionality of this organ in humans. Conclusion The vomeronasal organ, although a small and enigmatic structure within the human nasal cavity, holds great potential for unraveling the complexities of chemical communication and pheromonal perception. While its functionality in humans is a subject of ongoing debate, this organ remains an intriguing area of research. Continued scientific investigations into the Vomeronasal Organ’s anatomy, molecular biology, and evolutionary history will shed light on its true significance and potential impact on human behavior. Library Anatomy Anesthesiology Biochemistry Cardiology Dermatology Emergency Endocrinology ENT Examinations Forensic Med. Obs. & Gynae. Hematology Medicine Microbiology Nephrology Neurology Oncology Ophthalmology Orthopaedics Paediatrics Parasitology Pathology Pharmacology Physiology Psychiatry Pulmonology Radiology Rheumatology Surgery
Read More