- Newsletter
Celestamine
Celestamine belongs to the steroid family drugs and it contains Betamethasone and dexchlorpheniramine maleate as active ingredients. Celestamine (Betamethasone/dexchlorpheniramine) is commonly used to treat hypersensitivity or allergic reactions and inflammatory conditions.
Mechanism of action
Betamethasone which is an active ingredient of Celestamine is a synthetic glucocorticoid (steroids) with metabolic, immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities. Betamethasone binds to a specific intracellular glucocorticoid receptors and subsequently binds to DNA to modify gene expression which induced the synthesis of certain anti-inflammatory proteins while the synthesis of some inflammatory mediators is reduced. Therefore Betamethasone causes overall reduction in autoimmune reactions and chronic inflammation, thus reduces natural immune response of the body.
Dexchlorpheniramine is an alkylamine, and first-generation histamine receptor antagonist with anti-allergic activity. Dexchlorpheniramine competitively antagonises H1 receptors, thereby inhibiting the actions of histamine on H1 Histamine receptors on bronchial smooth muscle, capillaries and gastrointestinal smooth muscle. The antagonistic action of Dexchlorpheniramine inhibits the actions of endogenous histamine, thereby preventing histamine-induced bronchoconstriction, vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, and GI smooth muscle spasms, therefore used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria.
We’ve discussed the pharmacology of most common & essential drugs, & their Mechanism of actions, contraindications, cautions, side effects, use in pregnancy, use in breast feeding, adult dose, pediatric dose in our Pharmacology Made Easy eBook.
Betamethasone is used as an ingredient of Celestamine in some countries such as :
- Brazil
- Chile
- Hong Kong
- Indonesia
- Japan
- Paraguay
- Philippines
- South Africa
- Venezuela
Dexchlorpheniramine is used as an ingredient of Celestamine in Hong Kong.
Indications / Diseases where Celestamine is used:
- Perennial allergic rhinitis
- Severe bronchial asthma
- Serum sickness
- Hay fever (pollenosis)
- Drug reactions
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
- Contact dermatitis
- Inflammatory ocular disorders
- Iridocyclitis
- Uveitis
- Keratitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Non-granulomatous iritis
- Chorioretinitis and
- Choroiditis
Celestamine Dosage
Dose of Celestamine depends on the patient’s response to the drug and the severity of the illness.
- In the case, the conditions are better; the dosage should be reduced little by little until it is reduced to a minimum.
- After reaching the lowest dose, it should be suspended slowly.
- For people older than 12 years, an initial dose of 1 or 2 tablets (1 or 2 tablespoons) is prescribed for four times a day.
- It is best to take the dose after a filling meal or at bedtime.
- Do not increase the dose of Celestamine Ns in more than eight tablets or 8 tablespoons in the case of Celestamine Ns syrup.
- For children between 6 and 12 years, a dose of ½ tablet (1/2 tablespoon) should be administered three times a day. The dose should not exceed more than 4 tablets or 4 tablespoons in the case of syrup.
- For children between 2 and 6 years old, a dose of ¼ or ½ tablespoon should be administered three times a day. The general dosage should not be more than two tablespoons.
Summary of Celestamine dosage :
| Age | Dose | Frequency | Maximum Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| >12 years | 1 or 2 tablets (1 or 2 tablespoons) | 4 times/day | 8 tablets or 8 tablespoons |
| 6 - 12 years | ½ tablet (1/2 tablespoon) | 3 times/day | 4 tablets or 4 tablespoons |
| 2 - 6 years | ¼ or ½ tablespoon | 3 times/day | 2 tablespoons |
Special precautions
If celestamine contains Betamathasone :
As it contains Betamethasone as an active ingredient, adjustments of dosages in both adults and children may be required with remission or exacerbation of the clinical condition. Also, we should consider each patient’s individual response to therapy and exposure of the patient to psychological or physical stress such as injury, surgery or serious infection.
Betamethasone is a Corticosteroid, so we should monitor the patient for at least up to one year following the discontinuation of long-term or high-dose corticosteroid therapy.
Since complications of glucocorticoid therapy are dependent on duration and dosage of treatment, doctor should make the decision of risk or benefit for with each patient and their associated comorbidities.
Since high dose or long-term corticosteroid therapy is associated with many side effects like osteoporosis (fragile bones), hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes etc. the lowest possible dose of corticosteroid should be used to control the condition under treatment. A gradual reduction of dosage is recommended.
When the drugs are used in patients who have other comorbidities like hypothyroidism and cirrhosis, adverse effects of corticosteroids are increased.
Patients who take corticosteroids should be cautious if it’s used in patients with ocular herpes simplex because of possible risk of corneal perforation.
Psychological derangements also reported with corticosteroid therapy and those who already have emotional instability or psychotic tendencies may be aggravated by corticosteroid drugs like betamethasone/celestamine preparations.
These drugs should be used with caution conditions such as diverticulitis, fresh intestinal anastomoses, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, if there is a possible impending perforation, other pyogenic infection, abscess, or active or latent peptic ulcer disease, myasthenia gravis, osteoporosis, hypertension and renal insufficiency.
Since Corticosteroids are immunosuppressive agents, they may mask some signs of ongoing infection, and new infections may also appear during use. When corticosteroids are used, decreased resistance and inability to localize infection may occur.
Prolonged use of corticosteroid may lead to glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, posterior subcapsular cataracts (mainly in children) and may increase the chance of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses.
Elevation of blood pressure, retention of salt and water, and increased excretion of potassium which lead to hypokalemic complications may also occur with average and large doses of corticosteroids.
However, these side effects are less likely to occur when synthetic derivatives of corticosteroids are used except when used in large doses.
Supplementation of potassium and restriction of Dietary salt may be considered for these patients. All corticosteroids will increase excretion of calcium. So, it’s advised to take calcium supplements or calcium rich foods to prevent complications that can occur with long term calcium deficiency.
Since corticosteroids have immunosuppressive actions, patients should never be vaccinated for small pox. Other immunization procedures also should never be undertaken in patients who receive treatments with corticosteroids like betamethasone, celestamine etc., especially high doses, because of lack of antibody response and possible risk of neurological complications.
Patients who are on treatment with immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids should be warned and they should avoid exposure to chicken pox or measles. If exposed, they should immediately obtain medical advice as it might end up in serious complications. This is particularly important in children, elderly patients and patients who are already on immunosuppressive state like diabetes mellitus.
Treatment with Corticosteroid is in active tuberculosis should be restricted to those patients with disseminated or fulminating tuberculosis in which the corticosteroid is used in conjunction with an appropriate antituberculous regimen.
If corticosteroids are used in patients with latent tuberculosis, close monitoring is necessary since reactivation of the disease may occur due to suppression of immune system. Patients should receive chemoprophylaxis during prolonged corticosteroid therapy.
Growth and development of children who receive corticosteroid therapy for a prolonged period should be assessed carefully, since administration of corticosteroid can disturb the growth rates and inhibit the production of endogenous corticosteroids in these patients.
Celestamine should not be used in newborn and premature infants.
Corticosteroid therapy may alter the motility and number of spermatozoa.
If Celestamine contains Dexchlorpheniramine Maleate :
Celestamine products containing Betamethasone/Dexchlorphenamine Maleate should be used with caution in patients with pyloroduodenal obstruction, peptic ulcer disease, narrow angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy or bladder neck obstruction, cardiovascular disease including hypertension, in those with increased intraocular pressure or hyperthyroidism.
Patients should be warned about involving in activities requiring mental alertness, such as driving vehicles or operating machines etc.
Dexchlorpheniramine is a first-generation histamine receptor antagonist which crosses the blood brain barrier and causes dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in patients over 60 years of age.
Side effects of Celestamine
- Nausea and vomiting are common side effects.
- Increased sweating
- It can produce a sedative effect in which a person is always sleepy or drowsy.
- In some people, an alteration in electrolyte and fluid balance is also seen.
- Muscle problems such as loss of muscle mass, weakness of muscle and rupture of the tendon are common.
- Sometimes depression, mood swings and some other psychological problems are also seen in Celestamine users.
- In cases of women, menstrual irregularity is also common
- Some people also complain of vertigo and headache.
- There are also complains distension of the abdomen.
- There are also cases of Peptic ulcer, constipation and irritable bowel syndrome can occur.
- Delayed wound healing is also seen.
- Skin discoloration, thinning of the skin are some of the common complains of Celestamine.
Overdosage
Celestamine is a combination of Betamethasone/Dexchlorphenamine Maleate. So both components are responsible for the potential toxicities.
Overdosage reactions with Dexchlorphenamine Maleate may vary from depression of central nervous system such as sedation, respiratory depression, reduced mental alertness, cardiovascular collapse and stimulation of central nervous system such as insomnia, hallucinations, tremors, convulsions to death.
Other signs and symptoms of Dexchlorphenamine Maleate overdosage include may include tinnitus, dizziness, ataxia, blurred vision and hypotension. In adults, it causes depression with drowsiness and coma, and an excitement phase leading to convulsions followed by depression may occur. In children, stimulation if central nervous system is dominant where it causes atropine-like signs and symptoms such as dry mouth, fixed dilated pupils,flushing, fever and gastrointestinal symptoms. Hallucinations, incoordination, and convulsions may also occur with Dexchlorphenamine Maleate toxicity. In adults, it causes depression with drowsiness and coma, and an excitement phase may lead to convulsions followed by depression may occur.
Single toxic dosage of betamethasone is not expected to cause acute problems. However, at most extreme dosages, signs and symptoms of corticosteroid toxicity is seen.
Treatment of Acute Overdosage
If the patient is conscious, immediately induce emesis. Gastric lavage may also be done. Dialysis is not shown to be helpful in Celestamine toxicity.
Stimulants should be avoided. Treatment of the signs and symptoms of overdosage is symptomatic and supportive. If the patient is hypotensive, vasopressors can be used. Convulsions are best treated with a short-acting depressant, such as thiopental.
Fluida maintenance should be perfectly done and electrolytes should be monitored in serum and urine, with particular attention to potassium and sodium balance. If there is electrolyte imbalance, treat immediately.
Contraindications
- Never use this drug in a patient who is having any fungal infections in the body.
- Should not be used in newborn and premature infants.
- Using Celestamine in patients who have shown hypersensitivity to Betamethasone or Dexchlorphenamine Maleate or any chemical compounds similar to Celestamine should be avoided.
- Patients who are on therapy with Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
Drug and Food Interactions of Celestamine
Celestamine may interact with several other drugs and foods that can increase the risk of side effects. To avoid the harmful drug interactions, yo should always inform your doctor about the drugs that you are taking currently.
Medications that may cause drug interactions with Celestamine are,
- Cardiac glycosides enhance arrhythmias or digitalis toxicity.
- Phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampicin, ephedrine enhance the metabolism of Celestamine (Betamethasone/ dexchlorpheniramine).
- Coumarins, aspirin, NSAIDs, antidiabetic drugs.
Foods or alcohol will also interact with Celestamine and increase the risk for serious side effects.
Some diseases or health conditions can alter the way the drug works. It is important to inform your doctor about the diseases you have especially if you have liver or kidney disease, diabetes, tuberculosis, glaucoma, osteoporosis, cataract, thyroid diseases, stomach problems (ulcer, bleeding), diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis, Chest congestion, heart problems, depression, mental sickness, high blood pressure etc
SOME COMMONLY ASKED QUESTIONS BY PATIENTS
How to store Celestamine?
Celestamine should be stored at room temperature away from direct light and moisture. To prevent damage of the drug, it should not be stored in the bathroom or the freezer. It is important to check the product package for instructions on storage, or ask your pharmacist as there are different brands of Celestamine.
For safety, keep all medicines away from children and pets.
Do not flush Celestamine down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. It is important to properly discard the drug when it is expired or no longer needed. Seek advice from the pharmacist for more details on how to discard the drug safely.
How should I take Celestamine® (Betamethasone/ dexchlorpheniramine?
It comes as a tablet to take by mouth, should be taken with food, after meals or at bedtime.
Is it safe to use Celestamine during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Celestamine is not safe to take if you are breastfeeding or planning to start breastfeeding. Celestamine is a corticosteroid that can harm the fetus or an infant. This drug can also interrupt the normal growth of a newborn baby. Always consult a doctor before using Celestamine if you are a breastfeeding mother.
Is Celestamine addictive?
No, Celestamine doesn’t cause addiction, but it may cause sedation and drowsiness.
Does Celestamine make you sleepy?
Yes. Celestamine may cause sedation and drowsiness.
Is Celestamine good for cough?
Celestamine is used as mixtures with other cough syrups to treat cough. Celestamine is also used to treat other respiratory conditions such as allergic rhinitis and
severe Bronchial Asthma
How long can I take Celestamine?
Do not take for more than 7 days in a row. If your symptoms do not improve after 7 days of treatment or if you have any of the side effects we mentioned above, consult your doctor.
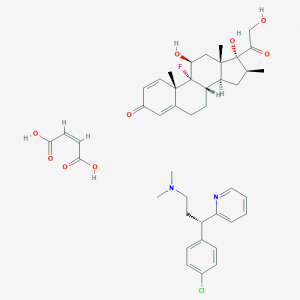
Additional biochemical information about Celestamine
Chemical Names:
- Celestamine
- Betamethasone / dexchlorpheniramine
- Betamethasone / dexchlorpheniramine maleate
- Betamethasone mixture with dexchlorpheniramine maleate
- SCHEMBL3361523
- 62682-62-6
Molecular Formula:
C42H52ClFN2O9 Molecular Weight:
783.331 g/mol

- Library

